Samsung Galaxy SII (samsung-i9100)
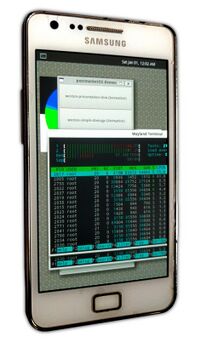 First photo ever released of postmarketOS (from the original introduction post). | |
| Manufacturer | Samsung |
|---|---|
| Name | Galaxy S II |
| Codename | samsung-i9100 |
| Released | 2011 |
| Hardware | |
| Chipset | Exynos 4210 Dual |
| CPU | Dual-core 1.2 GHz Cortex-A9 |
| GPU | Mali-400 MP4 |
| Display | 480x800 AMOLED |
| Storage | 16/32 GB |
| Memory | 1 GB |
| Architecture | armv7 |
| Software | |
| Original software | Android 2.3.4 |
| postmarketOS | |
| Category | testing |
| Pre-built images | no |
| Mainline | partial |
| Unixbench Whet/Dhry score | 542.5 |
| Flashing |
No data |
|---|---|
| USB Networking |
Works |
| Internal storage |
No data |
| SD card |
No data |
| Battery |
No data |
| Screen |
Works |
| Touchscreen |
Works |
| Multimedia | |
| 3D Acceleration |
No data |
| Audio |
No data |
| Camera |
No data |
| Camera Flash |
No data |
| Connectivity | |
| WiFi |
Works |
| Bluetooth |
No data |
| GPS |
No data |
| NFC |
No data |
| Modem | |
| Calls |
No data |
| SMS |
No data |
| Mobile data |
No data |
| Miscellaneous | |
| FDE |
Partial |
| USB OTG |
No data |
| HDMI/DP |
No data |
| Sensors | |
| Accelerometer |
Works |
| Magnetometer |
No data |
| Ambient Light |
No data |
| Proximity |
No data |
| Hall Effect |
No data |
| Haptics |
No data |
| Barometer |
No data |
Contributors
- ollieparanoid
- veggie
Device Owners
- Bastindo (Notes: Good condition, running Android 13)
- Clygro (Notes: 16GB Lineage OS Oreo based)
- Debiansh (Notes: Notes: Possible future test subject, bootloader unlocked, running LineageOS 17.1)
- EnderNightLord
- Hacker420 (Notes: LCD not working.)
- JonesV
- Kekson1a
- KenOokamiHoro (Notes: Running Replicant 6.0)
- Koalp
- MartijnBraam
- Newblicious
- Ollieparanoid
- Onny
- Oxr463
- Pairman (Notes: 1+16GB, Android)
- PL (Notes: Fine, but need a battery to start it.)
- Rudloff
- Russanandres (Notes: CyanogenMod 7 non booting)
- Sputnik1973 (Notes: No screen, no power button, no battery and maybe dead motherboard.)
- Tacokoneko (Notes: Samsung Galaxy S II Epic 4G Touch (d710))
- Timbz
- UltrasonicMadness (Notes: GT-I9100P, successfully working with MHL on stock firmware)
- Veselcraft (Notes: bad battery, 16 gb)
- Vladuwka12 (Notes: 16 GB, Running Replicant 6.0)
Status
What works
- Installation to sdcard (
pmbootstrap install --sdcard=/dev/mmcblk...) - Installation to device memory (partial)
- Touchscreen
- Weston (only on SD card)
- XWayland
- Wifi
- Display brightness control
- Accerelometer sensor
- rtc
- Xfce
What does not work
- Audio, bluetooth, modem, ...
- MHL (Video-out)
- See "Hardware specifications" for ideas how to get them working.
- Auto resizing partitions during installation to device memory (probably)
Installation
How to enter flash mode
- Connect a USB cable
- Make sure, the device is powered off
- Hold power + Home + volume down
- When prompted, release all buttons and press volume up
Step by step guide for Flashing via netcat (#456)
| If you get a "no space left on device" error, see #928. |
The normal installation does not work yet (#581, we might fix that in the future with our own flashing method which basically automatizes the netcat method). Right now you have the following options. If you use any of these, please expand the wiki with details.
- use
pmbootstrap install --sdcard(you will need a real sd card, but this is the easiest method) - use the netcat method (see below)
- use the recovery zip installer (you need to install a recovery like TWRP on your device, then run
pmbootstrap install --android-recovery-zipandpmbootstrap flasher --method=adb sideload.)
- Build image (on your computer)
-- Install pmboostrap
$ git clone https://gitlab.com/postmarketOS/pmbootstrap.git
-- Change working directory to the pmboostrap
$ cd pmbootstrap/
-- Configure
$ ./pmbootstrap.py init [18:27:09] Device [samsung-i9100]: samsung-i9100 [18:27:45] User interface [weston]: weston [18:28:05] Work path [/home/<USER>/.local/var/pmbootstrap]: [18:28:29] Jobs [5]: [18:28:46] Timestamp based rebuilds (y/n) [y]: [18:29:05] Extra packages [none]:
-- Prepare the installation
$ ./pmbootstrap.py install
- Flash to phone memory - This will replace (break) your current phone system! This uses the alternative flash method because it currently doesn't seem to work with heimdall - https://gitlab.com/BenjaminDobell/Heimdall/issues/418
-- Set phone to ODIN mode
1. Turn off phone 2. Connect USB cable 3. Hold VOLUME_DOWN + HOME + POWER until you get Warning!! screen 4. Push VOLUME_UP to continue to ODIN mode screen
-- Setup image for NETCAT flash method
$ ./pmbootstrap.py initfs hook_add debug-shell
-- Flash Kernel and Recovery (phone will reboot to screen "boot partition not found")
$ ./pmbootstrap.py flasher flash_kernel
-- Check USB network connection to phone
ping 172.16.42.1
(if it does not ping, try replugging usb cable few times)
-- Connect to phone with telnet
$ telnet 172.16.42.1
-- Start netcat to listen for image (on the phone) /dev/mmcblk0p9 should be FACTORYFS partition. Check by running fdisk -l /dev/mmcblk0
/ # nc -v -l -p 60000 > /dev/mmcblk0p9
-- Switch to pmboostrap chroot (on the computer in another terminal)
$ ./pmbootstrap.py chroot --suffix native
-- Install pv in the chroot
/ # apk add pv
-- Send image from computer to netcat (via the chroot)
/ # pv /home/pmos/rootfs/samsung-i9100.img | nc 172.16.42.1 60000
-- Close both nc with CTRL+C when transfer finishes and reboot the phone with power button
Boot process
We're using the heimdall-isorec flash method, see deviceinfo_flash_methods for more information.
Mainline kernel
The user Sekilsgs2 on Github created a mainline kernel port, based on the older kernel version 4.2. Using ArchLinux, I was still able to compile and flash the kernel using following commands:
$ git clone https://github.com/Sekilsgs2/i9100_kernel_mainline_port.git $ cd i9100_kernel_mainline_port $ export ARCH=arm $ export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-eabi- $ make i9100_defconfig $ make -j6 $ cat arch/arm/boot/zImage arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4210-i9100.dtb > zimage $ mkimage -A arm -O linux -T kernel -C none -a 0x40008000 -e 0x40008000 -n Linux-android-sucks -d zimage boot.img $ make modules_install INSTALL_MOD_PATH=../ $ heimdall flash --RECOVERY boot.img
It is also possible to use a more recent mainline kernel version. Therefore we will have to checkout the latest sources and download the device tree file:
$ git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux-stable.git $ cd linux-stable $ git checkout tags/5.4.5 $ wget "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Sekilsgs2/i9100_kernel_mainline_port/6c02dad36b8a76a6f50d26ff1b9abb0d30aacbc9/arch/arm/configs/i9100_defconfig" -O arch/arm/configs/i9100_defconfig $ wget "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Sekilsgs2/i9100_kernel_mainline_port/master/arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4210-i9100.dts" -O arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4210-i9100.dts $ wget "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Sekilsgs2/i9100_kernel_mainline_port/master/arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4210.dtsi" -O arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4210.dtsi # patch file arch/arm/boot/dts/Makefile $ export ARCH=arm $ export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-eabi- $ make i9100_defconfig $ make -j6 $ make dtbs $ cat arch/arm/boot/zImage arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4210-i9100.dtb > zimage $ mkimage -A arm -O linux -T kernel -C none -a 0x40008000 -e 0x40008000 -n Linux-android-sucks -d zimage boot.img
make modules_install INSTALL_MOD_PATH=../
$ heimdall flash --kernel u-boot.bin
Unfortunately some things doesn't work here any more. Using a keyboard with USB-OTG fails and also the screen output is up-side-down. I haven't yet found the fixes made to the custom 4.2 port which I have to reapply :(
Meanwhile Paul Cercueil is submitting an updated version of the device tree file upstream. As of March 2020, it is not yet clear when it will be accepted.
Firmware files
Proprietary firmware files are needed to get Wifi and Bluetooth working with the mainline kernel. In the following commands, I download them to the ArchLinuxARM root filesystem before booting the device. This should also work for postmarketOS:
$ wget "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TheMuppets/proprietary_vendor_samsung/cm-14.1/i9100/proprietary/system/etc/wifi/nvram_net.txt" -O /usr/lib/firmware/brcm/brcmfmac4330-sdio.samsung,i9100.txt $ wget "https://github.com/TheMuppets/proprietary_vendor_samsung/raw/lineage-17.0/i9100/proprietary/system/etc/wifi/bcmdhd_sta.bin" -O /usr/lib/firmware/brcm/brcmfmac4330-sdio.bin # for wifi $ wget "https://github.com/respeaker/rkbin/raw/master/firmware/bluetooth/BCM4330B1.hcd" -O /usr/lib/firmware/brcm/BCM4330B1.hcd # for bluetooth
U-Boot bootloader (legacy)
Sekilsgs2 on Github created a u-boot bootloader port, based on the work done by the user astarasikov at this repository. On Archlinux I was able to compile the older U-Boot version using following commands:
$ pacman -U dtc-1.4.1-1-x86_64.pkg.tar.xz # downgrade to older version $ pacman -S gcc-arm-none-eabi-bin-49 # older gcc version $ git clone https://github.com/Sekilsgs2/i9100-uboot.git $ cd i9100-uboot $ export PATH="/usr/local/arm/gcc-arm-none-eabi-4_9-2015q3/bin:$PATH" $ export ARCH=arm $ export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-eabi- $ make galaxys2_config $ make galaxys2 $ heimdall flash --KERNEL u-boot.bin
After that, u-boot is booting, showing a nice bootloader menu which can be controlled by using the arrow keys. Configuring the boot options is done by editing the file include/configs/galaxys2.h. The critical part for me was to change boot parameters in the section "boot_android" to something like this:
root=/dev/mmcblk1p1 rw rootfstype=ext4 rootwait init=/sbin/init ;
Where /dev/mmcblk1p1 was the ext4 partition with the root filesystem on the sd-card.
User:Onny is interested in porting the i9100 u-boot patches to newer versions of u-boot but currently u-boot fails with the newer s5p_sdhci driver introduced in newer versions, see Github issue here.
Sekilsgs2 is also working on (March 2020) supporting the Galaxy S2 in the latest u-boot version.
TALUAtGitHub has a recent commit (March 2020) git commit that might be helpful [1]
Usage
Wifi
- Create conf for wpa_supplicant
$ wpa_passphrase "SSID" "password" > wifi
Note : If you are connecting to a hidden wireless network, make sure to add line "scan_ssid=1" after the ssid line in your generated conf file
- Connect to wifi AP
$ sudo wpa_supplicant -i wlan0 -c wifi &
- Get ip address from dhcp server (in another terminal)
$ sudo udhcpc -i wlan0
To set wifi connection to start automatically on boot, please refer here wifi
Modem
Using Ofono: Best way seems to get Samsung IPC modem support from the patchset https://lists.ofono.org/pipermail/ofono/2012-September/013766.html (but it was not accepted) and does not build https://github.com/tssk/pmbootstrap/commits/device-samsung-i9100_modem . I would appreciate help from someone that understands C.
Second idea was to build Andoird RIL + Samsung RIL and get ofono working with ofono-ril support - https://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/Samsung-RIL .
GPS
https://univers-libre.net/posts/galaxy-s2-gps-on-replicant.html
https://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/GSD4t
https://github.com/mnalis/gsd4t_parser
https://redmine.replicant.us/boards/21/topics/897
Setting the hardware clock
If you have already setup chrony and if your hardware clock doesn't have the time set you can set it with,
localhost:~# hwclock -w # Write the current system time to the hardware clock
Setting the display brightness
To adjust display brightness write a value between 0-255 to file given below,
localhost:~# echo 0 > /sys/class/backlight/panel/brightness #set the display to its lowest brightness
localhost:~# echo 255 > /sys/class/backlight/panel/brightness #set the display to maximum brightness
Reading Accelerometer sensor
Accelerometer sensor data can read from following file
localhost:~$ cat /sys/class/accelerometer/accelerometer/acc_file
Hardware specifications
| This device is supported by Replicant. With some more research we should be able to get most stuff running with their free software userland drivers. |
SoC
Samsung Exynos 4 Dual 45 nm (GT-I9100, SHW-M250S/K/L) source
CPU
1.2 GHz dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 (GT-I9100, GT-I9105, GT-I9100G, SHW-M250S/K/L) source
GPU
ARM Mali-400 MP4 (GT-I9100, SHW-M250S/K/L) source
WiFi / Bluetooth / FM radio
Broadcom BCM4330 (SWB-B42) Bluetooth 4.0 Dual Band WLAN FM source source
Driver? - https://wireless.wiki.kernel.org/en/users/drivers/brcm80211
Firmware - https://android.googlesource.com/platform/hardware/broadcom/wlan/+/master/bcmdhd/firmware/bcm4330/
Memory
1 GB RAM [2]
Storage
16 GB or 32 GB flash memory [3]
Removable storage
microSD (up to 128 GB SDXC) [4]
Modem
- XMM6260 [5]
- aka "X-GOLD 626", and it's also used in Nexus 7 [6]
- it seems to be supported by the mainline kernel (big questionmark here) [7]
Audio
- Yamaha MC1N2
- The Android kernel exposes the alsa API.
- But when you play with the volume sliders in alsamixer, nothing happens
- /dev/snd/hwC0D0 implements hardware-specific controls (via ioctl) [8] (check the link for a free software Android userspace driver)
- We could write a daemon, that watches the alsa sound levels, and unmutes channels (speaker, headphones etc.) via hwC0D0 as necessary. (This will only work with the downstream kernel, the sound is probably not implemented in the upstream kernel at all?)
- Maybe all this is overkill and the strategy from Audio works as well.
Light / proximity sensor
the CM3663 sensor is being use and there is no driver in mainline. A downstream driver is available here.
MHL
- Fairchild FSA3200UMX switch [9]
- Maxim MAX8997 PMIC [10]
- Silicon Image 9244 transmitter [11]
- Should be all supported to a certain extent in mainline 4.15 kernel (of course the device is still stuck to 3.0 for the time being)
Serial / UART
It is not exactly clear yet where to find UART / serial on the device. For possible location see second image below (red rectangle). Nevertheless a good instruction on hardware teardown is available here. Follow this guide until step 5, than proceed with removing the black cover from the circuit board (see first image below).
-
Remove black cover (it is only glued)
-
UART possibly located in this field (red rectangle)
Photos
- Initramfs asking for the password via telnet
- Weston with various programs opened
- postmarketOS demo menu (XWayland)
- Firefox (XWayland)
- Weston-smoke demo
- Weston-smoke demo running on a d710
- xfce-ui running on i9100

